Quantitative easing (QE) has turn into synonymous with the COVID-19 pandemic because the blowout from the lockdowns stalled the expansion of the worldwide economic system and threatened to show right into a monetary disaster.
To artificially create financial progress, central banks started shopping for up authorities bonds and different securities, whereas governments started increasing the cash provide by printing extra money.
This was felt essentially the most within the U.S., the place the Federal Reserve elevated the speed of {dollars} in circulation by a file 27% between 2020 and 2021. The Fed’s stability sheet reached round $8.89 trillion on the finish of August 2022, a rise of over 106% from its $4.31 trillion dimension in March 2020.
None of this, nevertheless, managed to discourage a monetary disaster. Fueled by the continued battle in Ukraine, the present disaster is slowly gearing as much as turn into a full-blown recession.
To mitigate the results of its ineffective QE insurance policies, the Federal Reserve has launched into a quantitative tightening (QT) spree. Additionally known as stability sheet normalization, QT is a financial coverage that reduces the Fed’s financial reserves by promoting authorities bonds. Eradicating Treasurys from its money balances removes liquidity from the monetary market and, in concept, curbs inflation.
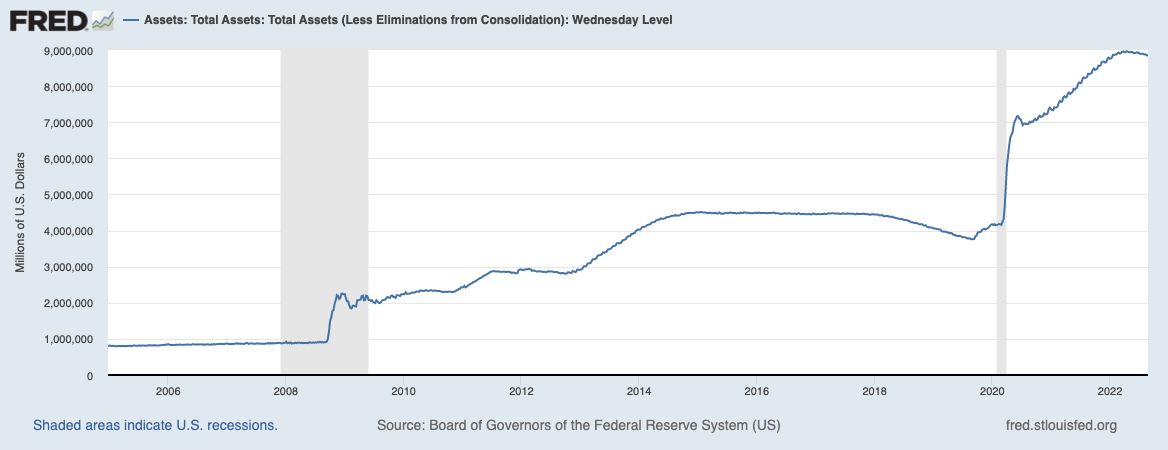
In Might this 12 months, the Fed introduced that it will start QT and lift the federal funds charge. Between June 2022 and June 2023, the Fed plans on letting round $1 trillion price of securities mature with out reinvestment. Jerome Powell, the Chairman of the Federal Reserve, estimated this is able to equal one 25-basis-point charge hike in how it will have an effect on the economic system. On the time, the cap was set at $30 billion monthly for Treasurys and $17.5 billion for mortgage-backed securities (MBS) for the primary three months.
Nonetheless, more and more worrying inflation has pushed the Fed to double its shrinking tempo for September, rising it from $47.5 billion to $95 billion. Because of this we will count on $35 billion in mortgage-based securities to be offloaded in a month. And whereas the market appears extra nervous about Treasurys, offloading the mortgage-backed securities may very well be what truly triggers a recession.
The risks of the Fed unloading mortgage-backed securities
Whereas mortgage-backed securities (MBS) have been a major a part of the monetary market within the U.S. for many years, it wasn’t till the 2007 monetary disaster that most of the people turned conscious of this monetary instrument.
A mortgage-backed safety is an asset-backed safety that’s backed by a group of mortgages. They’re created by aggregating an analogous group of mortgages from a single financial institution after which offered to teams that bundle them collectively right into a safety that buyers can purchase. These securities had been thought-about a sound funding earlier than the 2007 monetary disaster, as in contrast to bonds which paid out quarterly or semi-annual coupons, mortgage-backed securities paid out month-to-month.
Following the collapse of the housing market in 2007 and the next monetary disaster, MBS turned too tainted for personal sector buyers. To maintain rates of interest secure and stop additional collapse, the Federal Reserve stepped in as a purchaser of final resort and added $1 trillion in MBS to its stability sheet. This continued till 2017 when it began letting a few of its mortgage bonds expire.
The 2020 pandemic compelled the Fed to go on one other shopping for spree, including billions in MBS to its portfolio to inject money into an economic system scuffling with lockdowns. With inflation now hovering, the Fed is embarking on one other offloading spree to maintain rising costs at bay.
Along with permitting them to run out, the Fed can also be promoting the mortgage-backed securities in its portfolio to personal buyers. When non-public buyers purchase these mortgage bonds, it pulls money out of the general economic system — and will (not less than in concept) assist the Fed obtain precisely what it got down to do.
Nonetheless, the possibilities of the Fed’s plan truly working are reducing day-after-day.
Whereas offloading $35 billion in MBS each month may appear like it’s curbing inflation within the brief time period, it may have a detrimental impact on the already struggling housing market.
For the reason that starting of the 12 months, mortgage charges have elevated from 3% to five.25%. The leap to three% from a 2.75% fastened rate of interest was sufficient to lift pink flags for a lot of. A leap to five.25% and the potential to extend even larger signifies that a whole bunch of 1000’s of individuals may very well be pushed out of the housing market. The gravity of this drawback turns into clearer when taking a look at it as a proportion improve, and never as an absolute quantity — rates of interest have gone up 75% because the starting of the 12 months.
With mortgage funds 75% larger, the market may see many individuals defaulting on their funds and their properties at risk of foreclosures. If mass foreclosures like those we’ve seen in 2007 do occur, the U.S. housing market may very well be flooded with a contemporary provide of homes.
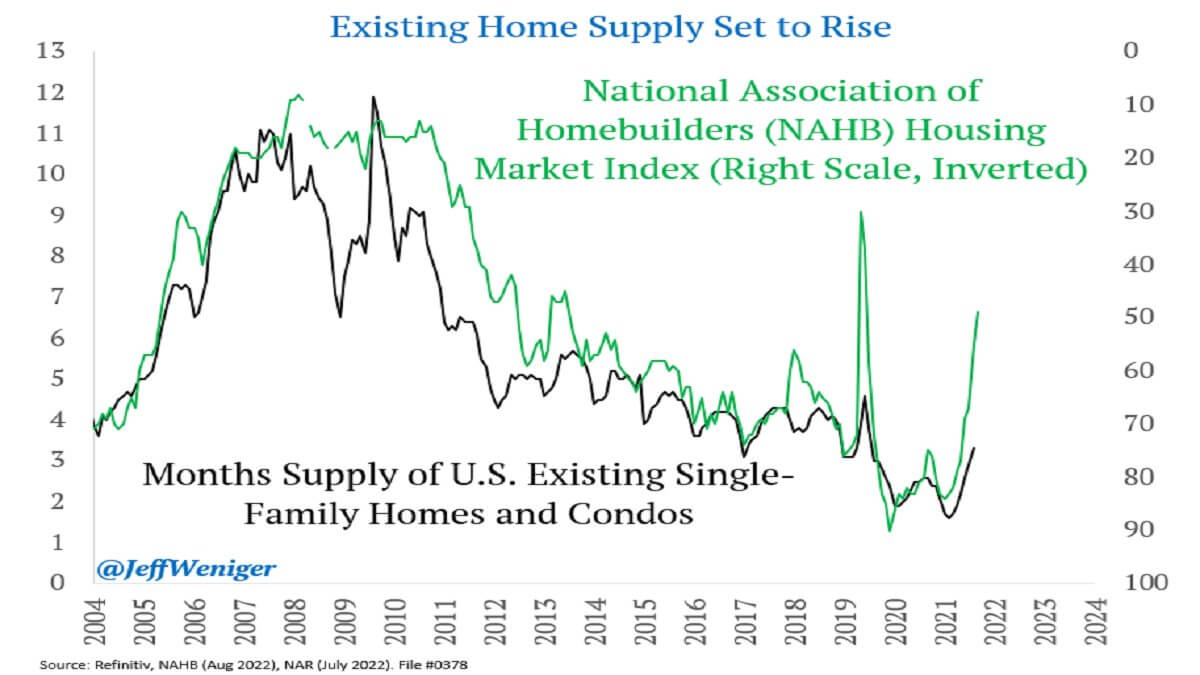
Information from the Nationwide Affiliation of Homebuilders (NAHB) exhibits that the month-to-month provide of single-family properties and condos within the U.S. has been on the rise since 2021. The NAHB Housing Market Index, which charges the relative stage of single-family house gross sales, has been reducing considerably because the starting of the 12 months, getting into its eighth straight month of decline.
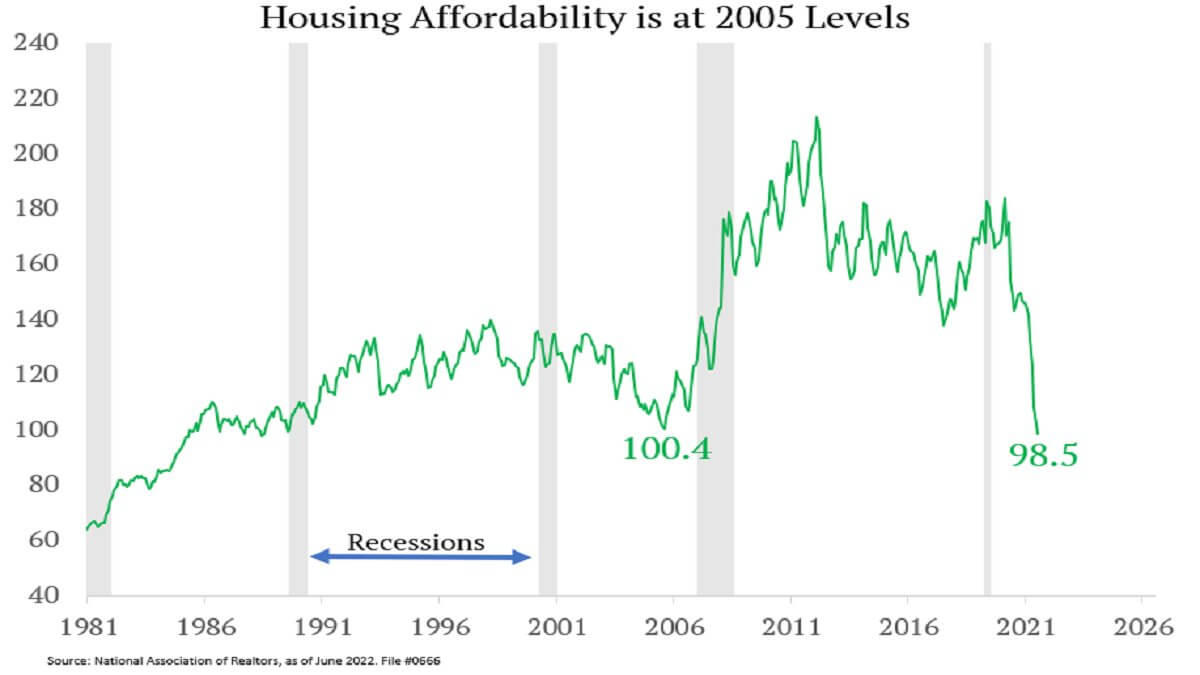
Based on knowledge from the Nationwide Affiliation of Realtors, housing affordability within the U.S. has reached its 2005 ranges, suggesting that housing costs may peak simply as they did in 2006.
Redfin and Zillow, the 2 largest actual property brokerages within the U.S., noticed their share value drop 79% and 46% because the starting of the 12 months. The difficulty that’s been brewing within the housing market since final summer time exhibits that the “smooth touchdown” the Fed is making an attempt to attain with QT shall be something however smooth. With increasingly more market circumstances lining up virtually completely with the circumstances seen in 2006, a brand new housing disaster may very well be ready across the nook. In its try to stabilize the monetary market, the Fed may inadvertently destabilize the housing one.
The results a housing disaster and a recession may have on the crypto market are arduous to foretell. Earlier market downturns have dragged cryptocurrencies down with them, however the digital asset market managed to get better extra rapidly than its conventional counterparts.
We may see the crypto market taking one other hit within the occasion of a full-blown recession. Nonetheless, foreign money devaluation may push extra folks to search for various “arduous belongings” — and discover what they’re searching for in crypto.

